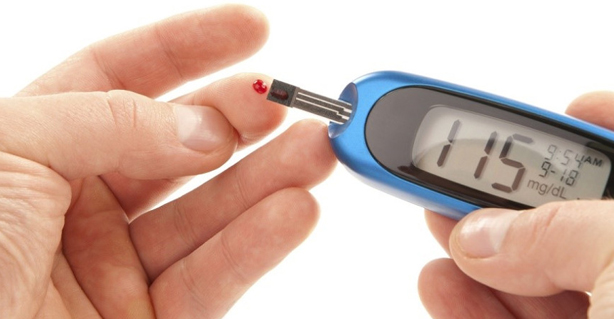
Diabetes might be one of the most talked about diseases across the world and especially in India, but awareness about the same can well be estimated by the fact that India today has more people with type-2 diabetes. The WHO also estimates that 80 per cent of diabetes deaths occur in low and middle-income countries and projects that such deaths will double between 2016 and 2030.
Interestingly, ZINC has long been an ingredient used in “older” insulins, such as Regular, NPH, and Lente. ZINC is also necessary for the formation of insulin in the pancreas’s beta cells. For these reasons, researchers have looked at the role of zinc supplementation in the prevention and treatment of Type 2 diabetes— but unfortunately, without success.
However, new light has been shed on the role of ZINC in diabetes. In this month’s issue of Diabetes Care, Finnish researchers followed 1,050 adults with Type 2 diabetes for seven years. During that time, 156 participants died from heart disease and 254 had fatal or nonfatal heart attacks. Blood ZINC levels were lower in people who died from heart disease compared to those who survived; also, ZINC levels were lower in those who had heart attacks. The authors of this study speculate that, possibly because ZINC has antioxidant properties, supplementation may be useful in warding off heart disease in people with Type 2 diabetes.
DIABETES has a harrowing background in India
The diabetes capital of the world with as many as 50 million people suffering from type-2 diabetes, India has a challenge to face. However, medical experts feel that timely detection and right management can go a long way in helping patients lead a normal life. Diabetes might be one of the most talked about diseases across the world and especially in India, but awareness about the same can well be estimated by the fact that India today has more people with type-2 diabetes (more than 50 million) than any other nation.
With the country having the highest number of diabetic patients in the world, the sugar disease is posing an enormous health problem to our country today. Often known as the diabetes capital of the world, India has been witnessing an alarming rise in incidence of diabetes according to the International Journal of Diabetes in Developing Countries. According to a World Health Organization (WHO) fact sheet on diabetes, an estimated 3.4 million deaths are caused due to high blood sugar.
The WHO also estimates that 80 per cent of diabetes deaths occur in low and middle-income countries and projects that such deaths will double between 2016 and 2030. It has been further estimated that the global burden of type-2 diabetes is expected to increase to 438 million by 2030 from 285 million people (recorded in 2010). Similarly, for India this increase is estimated to be 58%, from 51 million people in 2010 to 87 million in 2030. But
debates, discussions and deliberations aside, the fundamental thing is to know what exactly is diabetes.
To put it simply, it is a medical condition that is caused due to insufficient production and secretion of insulin from the pancreas in case of Type-I diabetes and defective response of insulin Type-2 diabetes. Under normal body circumstances, blood glucose levels are tightly controlled by insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. Insulin lowers the blood glucose level. When the blood glucose elevates (for example, after eating food), insulin is released from the pancreas to normalise the glucose level. In patients with diabetes, the absence or insufficient production of insulin causes hyperglycaemia.
Diabetes is a chronic medical condition, that is, it can be curbed at the initial level by introducing lifestyle changes and controlled after its incidence through medicines in early stages and administration of external insulin in advanced stages. But it would not be wrong to say that it cannot be cured completely and lasts a lifetime.
Diabetes mellitus is one of the world’s major diseases. It currently affects an estimated 143 million people worldwide and the number is growing rapidly. In India, about 5 per cent population suffers from diabetes. Medical health experts assert that regular check-ups and timely detection plays a vital role in controlling and managing the problem. Ironically, due to patient resistance and feeling of disbelief that ‘I can have diabetes too’, most patients tend to defer on detection and treatment that often leads to complications.
Practitioners feel that patient adherence to medication and lifestyle modifications play an important role in diabetes management and this can help them lead a normal life. Un-monitored prevalence of diabetes also results in increased risk of vascular complications like cardiovascular, renal, neural and visual disorders which are related to the duration of the disease.
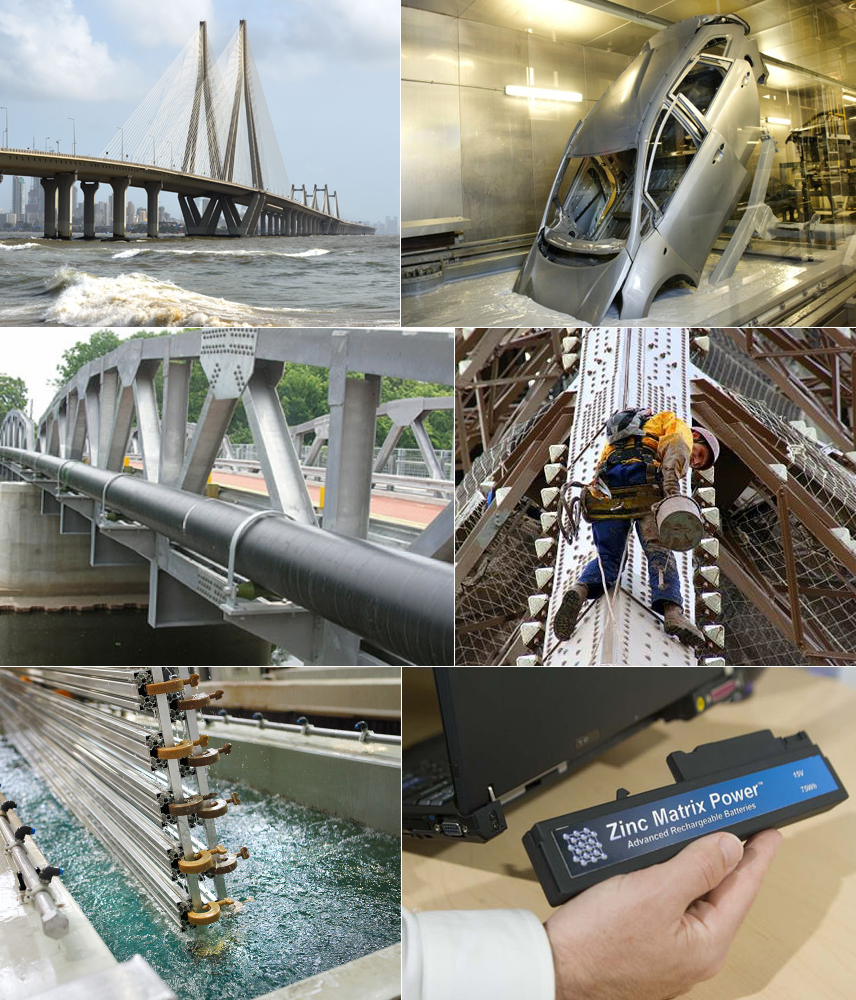





























































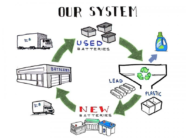









 One of the major sectors that is set to change is the automobile sector. Globally there has been a discrepancy in using galvanized car bodies. Indian car manufacturers use about 3% galvanized steel for the cars manufactured and sold in the domestic market. However, the same Indian car manufacturers use over 70% galvanized steel for the same models they export to markets in Europe, Asia and Africa, produced from the same stamping and assembly facilities. The car companies are not presently using galvanized steel for the domestic market because like other countries, Indian consumers are not demanding it. Stephen Wilkinson, Executive Director of International Zinc Association says, “Car makers in Europe, North America, Korea and Japan have been using galvanised steel for body panels for decades. These car companies provide anti-corrosion and perforation warranties for a minimum of 10 years. But there is no such protection for most cars made for the Indian consumers. Here the customers are advised to pay for extra coatings to protect the body of the car after purchase. More than 60% of the cars in India have surface rust which reduces steel strength and the life of the car.” In China, more vehicles are sold each year than the U.S. and Japan combined, and they rarely use galvanized steels, according to the International Zinc Association. The annual passenger vehicle sales will rise to 24 million in 2020 in China, from 19 million last year, as per McKinsey & Co. forecasts and only about one thirds of locally-manufactured autos use galvanized panels to prevent corrosion and rusting. China’s drivers will increasingly demand rust-proof cars in future according to report. Only about a third of locally-manufactured autos use galvanized panels to prevent corrosion and rusting. That’s good news for the price of zinc, the anti-corrosion fighter that’s already this year’s top performer among base metals. Domestic automakers in China, where more vehicles are sold each year than the U.S. and Japan combined, rarely use galvanized steels. Switching to the material would require about 350,000 metric tons a year of additional zinc, the association estimated last year. A similar move in India would need an extra 150,000 tons annually.
One of the major sectors that is set to change is the automobile sector. Globally there has been a discrepancy in using galvanized car bodies. Indian car manufacturers use about 3% galvanized steel for the cars manufactured and sold in the domestic market. However, the same Indian car manufacturers use over 70% galvanized steel for the same models they export to markets in Europe, Asia and Africa, produced from the same stamping and assembly facilities. The car companies are not presently using galvanized steel for the domestic market because like other countries, Indian consumers are not demanding it. Stephen Wilkinson, Executive Director of International Zinc Association says, “Car makers in Europe, North America, Korea and Japan have been using galvanised steel for body panels for decades. These car companies provide anti-corrosion and perforation warranties for a minimum of 10 years. But there is no such protection for most cars made for the Indian consumers. Here the customers are advised to pay for extra coatings to protect the body of the car after purchase. More than 60% of the cars in India have surface rust which reduces steel strength and the life of the car.” In China, more vehicles are sold each year than the U.S. and Japan combined, and they rarely use galvanized steels, according to the International Zinc Association. The annual passenger vehicle sales will rise to 24 million in 2020 in China, from 19 million last year, as per McKinsey & Co. forecasts and only about one thirds of locally-manufactured autos use galvanized panels to prevent corrosion and rusting. China’s drivers will increasingly demand rust-proof cars in future according to report. Only about a third of locally-manufactured autos use galvanized panels to prevent corrosion and rusting. That’s good news for the price of zinc, the anti-corrosion fighter that’s already this year’s top performer among base metals. Domestic automakers in China, where more vehicles are sold each year than the U.S. and Japan combined, rarely use galvanized steels. Switching to the material would require about 350,000 metric tons a year of additional zinc, the association estimated last year. A similar move in India would need an extra 150,000 tons annually.



































