We are cognisant that risk management is critical for realisation of organisation goals. The importance of early identification of probable risks, as well as timely formulation of strategic plans to mitigate the same, is important to be successful on this count. We, therefore, have in place a strong and sustainable risk management framework, supported by risk disclosure through various internal online platforms to allow timely escalations and actions. Risks are clearly defined with specific management targets and indicators, which are in turn mapped across categories, class, and their potential impact, and evaluated on a regular basis.
As per requirement of SEBI (LODR), the Board has formed a Risk Management Committee to oversee the mitigation plan for the risks faced by the Company. Risk Management is led by the Chief Risk Officer (CRO), who is part of the Risk Management Committee. The CRO’s roles and responsibilities include keeping the senior management aware of all existing and emerging risks at asset and business levels. The CRO additionally guides strategic business unit (SBU) heads, who are equally responsible for managing risk in their respective business units. Necessary awareness and specific training sessions are conducted periodically across all business units.
To ensure further transparency and critical assessment of risk, we have a group management assurance system that co-ordinates the risk management framework, which is reviewed annually by the Audit Committee on behalf of the Board. These efforts are further supported by a Board. Level Risk Management Committee comprising the CEO, CFO and Chairman of the Audit Committee. The Head of our group management assurance, along with CRO, CHRO, CCO, COO Mines and COO Smelters, is a permanent invitee. The Risk Management Committee discusses key events impacting the risk profile and emerging risks, and monitors progress against the planned action.
Hindustan Zinc’s risk management system is certified as per ISO 31000:2018
Our risk management framework is well-structured and allows us to identify, assess, categorise, address, and mitigate both positive opportunities and negative consequences associated with our business. These are regularly monitored, tracked, and reviewed through a robust Governance and Process architecture, with roles and responsibilities clearly defined for each stage.
We believe it is important for an organisation to be imbued with a culture of proactive risk management. At Hindustan Zinc, we foster such a culture through continuous and sustained initiatives aimed at creating awareness, discussing mitigation and encouraging discussion across the hierarchy.
Some of the key elements and policies that further propagate risk-awareness. These include:
To ensure continual strengthening of our risk mitigation and management framework, we clearly define risk management targets and indicators as part of our risk scorecard. Further, performance evaluation is undertaken at the management and higher levels on a regular basis.
Cybersecurity is vital in the digital age that characterises the increasingly connected world we live in. The COVID-19 pandemic, and the consequent rapid shift to remote working for employees, presented significant technological challenges across industries. At Hindustan Zinc, with our consistent investment in technology and stringent processes, we experienced no significant disruptions.
The operating and control systems at our mines increasingly leverage high-tech solutions. These systems, although crucial for operating the mines safely and efficiently, are vulnerable to evolving cyber threats and security breaches. Consequently, cybersecurity has emerged as one of our most significant business risks.
Cyber-related threats will continue to grow, with malicious actors targeting organisations with extortion through ransomware. Maintaining cybersecurity across our operations is an ongoing process, and we remain committed to ensure that our technology is protected from attacks, confidential information is safe, data integrity is protected, and business continuity is maintained through any disastrous event.
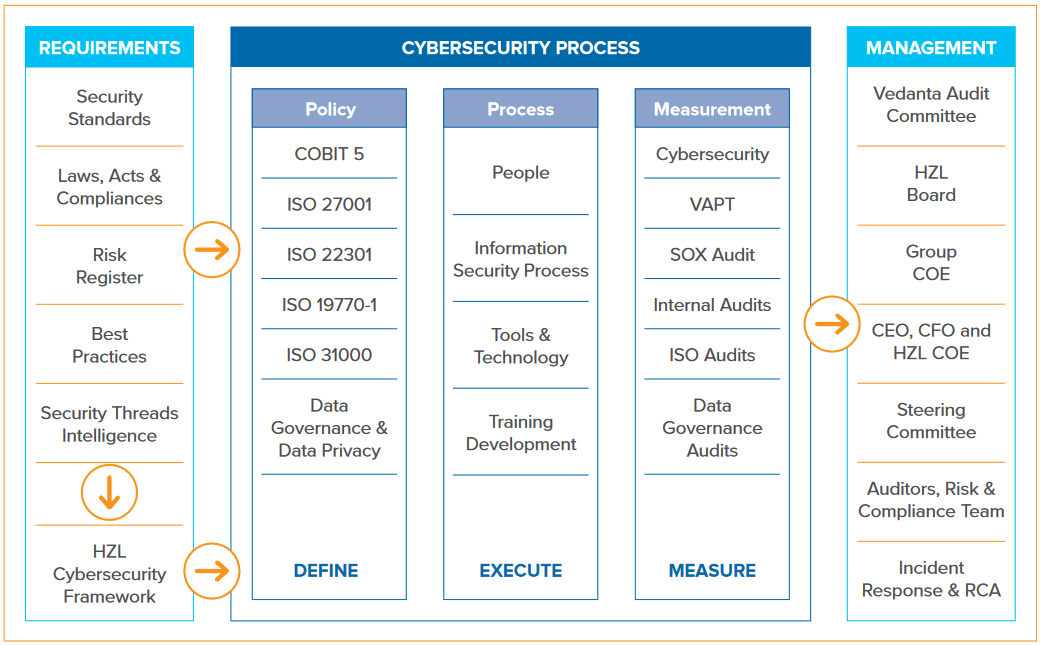
Our Cybersecurity Framework details a principle and objective-based approach to protect the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of all technology and data assets, including those we rely on in our operations. The standard is particularly applicable to all assets that are critical for business and operational resilience, as well as stability and regulatory compliance. The framework focusses on the risks and critical controls around our assets.
Additionally, several other standards and guidelines support the framework and govern HZL’s information technology and cybersecurity practices. These include the information security management and personal data privacy standards, disaster recovery and business continuity management, and risk management.
Hindustan Zinc received an Integrated ISO Certification, consisting of ISO 27001 (Information Security), ISO 22301 (DR & BCP), ISO 31000 (Risk Management) and ISO 27701 (Privacy Management), during 2021. We are committed to minimising business risks and have incorporated the NIST cybersecurity information framework into our cybersecurity operating model at all levels.
Our cyber programme focusses on four strategic areas aimed at enhancing cybersecurity capabilities across the business to minimise risks:
Risks and vulnerabilities are identified and addressed across the IT, OT, and digital landscape in line with the Company’s vulnerability management policy. Internal and external vulnerability assessment and penetrating testing (VAPT) programme, surveillance audit, assessment of IT general controls (ITGC) are carried out by globally reputed and recognised third-party agencies on an annual basis.
Observations and points emanating from risk controls matrix, review controls and open observations reported through various assessments and actions emerging from the annual IT risk assessment and DR/ BCP reviews are tracked as part of the CIO’s monthly review, in addition to the reviews carried out by other internal and external forums.
All security incidents are tracked and monitored till their logical closure, including root cause analysis and action plan to mitigate similar incidents in the future, under the incident management and data breach policy. Every reported incident is investigated by the CISO, and action is taken to address the incident reported through a common e-mail. Hindustan Zinc has also implemented multiple best-in-class tools and technologies (SIEM & DLP) to continually monitor critical IT assets and data movement. Such tools automatically generate incidents based on the rules.
Hindustan Zinc conducted a business impact analysis (BIA) for all critical IT systems and defined RPO and RTO for these systems in collaboration with, and on approval by respective system owners and functional business heads. Our business continuity plan (BCP) considers various risks, including technical, natural disasters and human risks including those related to external partners
To build the team’s capability to identify and report breaches, Hindustan Zinc has prepared a holistic Cybersecurity Awareness Plan, which is executed throughout the year. Awareness areas include all the important domains of IT and OT security and data governance. All new joinees are mandated to attend the cybersecurity training during their on- boarding process. Additionally, an online awareness training capsule on self-service mode is available to all users. The information security function tracks and monitors the status of the self-training conducted by the user, and accordingly carries out periodic follow-ups to propagate the learnings. Periodic trainings are also arranged through virtual classrooms on a voluntary / self-nomination basis. Guidance is circulated periodically to all users on how to classify information as per the information classification policy of the Company.