Given that our operations are dependent on the effective management of natural resources, we, at Hindustan Zinc, have prioritised environment protection as a key tenet of our ESG ethos. We are committed to mitigate the risks and impacts of our operations across the business value chain – right from the start of an operation to its closure and even beyond.
In the immediate term, we are focussed on accelerating actions to lower carbon emissions generated during our operations. Our environment conservation efforts are driven by a strategic thrust on minimising and mitigating our impact on water, land, air quality, climate, and biodiversity. We are also committed to building harmonious relations with our stakeholders, to reduce the environmental footprint of our operations by deploying resource management systems and controls.
The transition to net-zero carbon emissions will create additional demand opportunity for our products – zinc, lead and silver, with expected growth in solar PV panels and energy storage solutions.
At Hindustan Zinc, we have already embarked on several ambitious goals and action plans to steer our net-zero journey and mitigate the catastrophic effects of climate change. As a COP26 Business Leader, the Company has always been actively working towards tackling the repercussions of climate change. From setting steep targets to achieve business sustainability, we have established a stronger governance structure for the realisation of these goals. We have committed ourselves to the long-term target to reach net-zero emission by 2050, in line with the Business Ambition for 1.5 degrees Celsius campaign led by the Science-Based Targets initiative (SBTi) in partnership with the UN Global Compact and the ‘We Mean Business’ coalition.
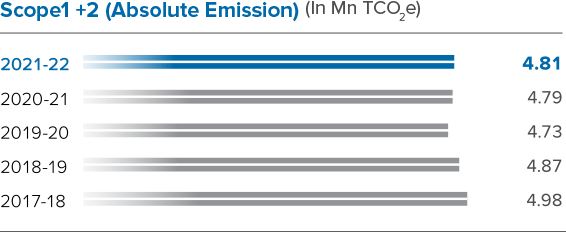
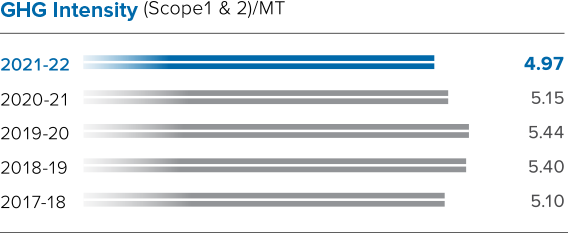
In the near-term, our 2025 targets include reducing GHG emissions, extending the implementation of our sustainability standards to our suppliers, reducing dependency on freshwater, besides moving towards zero waste to landfill, among others. Under Sustainability Goal 2025, we aim to achieve 0.5 Mn TCO2e GHG emission savings in our operations since the base year – 2017 – as part of our climate risk mitigation efforts.
Hindustan Zinc has a green power capacity of around 354.59 MW, which includes 273.5 MW of wind power (non-captive), 40.42 MW (captive) solar power and 40.67 MW of Waste Heat Recovery Power. All our wind and solar projects are registered under Gold Standard (GS), which is the most rigorous certification standard globally for carbon offset projects. The Gold Standard is an independent certification standard for carbon credits generated from CDM or VER projects. Our Captive Thermal, Solar and Waste Heat Recovery Power plants provide low-cost and reliable power to our operations. Our climate change risk assessment is aligned with guidelines by the Task Force on Climate-Related Financial Disclosures (TCFD), and we strive to continually expand our renewable power under our greenhouse gases reduction goals. In alignment with our vision, we are entering into a power purchase agreement with a company for supplying 200 megawatts of renewable power. With this collaboration, about 40% of our thermal power capacity will be taken over by renewable power by 2025. By 2030, about 80% to 90% of our thermal power will be replaced by renewable power.

Technology and digitalisation are key to strengthening our ESG footprint and creating a net-zero future. It is our ambition to convert all our mining equipment to battery-operated Electric Vehicles (EVs). To make our mining operations environment-friendly, we plan to invest US$ 1 billion over the next five years to induct electric and battery-operated equipment against that going for replacement and new purchase.
Electric Vehicles (EVs) are a globally recognised means to alleviate dependence on petroleum products and reduce CO2 emissions. Therefore, Hindustan Zinc signed a Memorandum of Understanding (MoU) with Epiroc Rock Drills AB, Normet Group Oy and Sandvik AB to introduce battery electric vehicles (BEV) in its underground mining operations. This makes Hindustan Zinc the first company in India to introduce battery-operated vehicles in underground mines. This partnership will allow the Company to replace diesel-powered equipment with electric vehicles, thus enabling safer and cleaner mining operations.
Along with Memorandums of Understanding signed with leading equipment manufacturers, the Company has also deployed passenger EV vehicles, EV forklifts and EV light motor vehicles in its operations.
To align our target with SBTi, we have partnered with CDP India under the SBTi Incubator programme to help accelerate our transition to a low-carbon economy. The incubator aims to achieve reduction of GHG emissions through the uptake of Science-based targets in the long-term, and to set corporates on the path of climate science-based emission reduction targets.
Meeting science-based targets in the context of a growing business can be difficult. Responding to this challenge, we have implemented a range of measures to reduce our Scope 1 and 2 emissions throughout the life cycle. We have made dedicated investments in enabling efficient use of energy and work on gainful utilisation of wastes using environment-friendly methods. This helps the Company steer its efforts towards the achievement of a circular economy in the lifecycle of its operations with the aim of enabling decarbonisation.
Our focus is on reprocessing tailing material for extracting left-over minerals, utilisation and sale of by-products for beneficial use, and collaboration with various corporations and industrial sectors for inter-usage of waste/by-products. The reduction in the quantum of waste that needs to be recycled or sent to landfills/incinerators leads to lesser energy consumption. By re-using the recycled material, the Company can save on emissions from production of virgin material.
During the year, the Company produced solar power of 80.92 million units, waste heat energy of 211.79 million units and wind power of 427.52 million units, leading to avoidance of 6.13 lac tonnes of GHG emission through green power. We achieved our highest green power (WHRB + wind + solar) in FY 2021-22 and the highest ever CERs through green power.

Strong governance system to drive the low-carbon economy strategy
Tier-1Board-level ESG committee
Tier-2Executive sustainability committee
Tier-3Energy and carbon community
Our environmental ethos is embedded in the organisational fabric, as we continue to take major strides in our journey to achieve the net-zero goal.
The Mine and Metal industry is energy intensive. As a leading player in this sector, we are investing in the latest technologies and processes – recognised as industry benchmarks – to scale energy efficiencies. We remain committed to efficient usage of energy and diversification of our energy portfolio to the extent possible. In line with this commitment, we are reducing our overall energy consumption, improving energy efficiency, and using green energy to help mitigate the impact of climate change. All our units are ISO 50001 certified.
To achieve our 2050 goal, we are taking regular initiatives to drive the transition towards renewable energy. We have approved a proposal for entering a long-term group captive renewable power development plan, up to a capacity of 200 MW. The project will be built under group captive norms on Build-Own-Operate (BOO) basis, through a special purpose vehicle (SPV). Hindustan Zinc will own 26% equity in the SPV. This project will constitute ~25% of our total power consumption, resulting in 1.2 million MT of carbon emission reduction.
Cleaner Fuel for Power Generation
Our target to achieve net-zero by 2050 is aligned with our emissions control journey that started with revamping of turbine followed by use of biomass as an alternative fuel in our captive power plant (CPP). It was a critical time when fossil fuel prices went abruptly high due to high demand in international industries coupled with lack of production due to local strictures and restriction on coal import by the government. It was during this time that the team at Hindustan Zinc started researching alternatives to sustain the business and reduce emission levels. With incremental increase in biomass consumption from 1% to 5%, we were able to reduce the coal consumption, its associated GHG emission and costs to move a step closer to our ESG goal.
Benefits
Our environmental ethos is embedded in the organisational fabric, as we continue to take major strides in our journey to achieve the net-zero goal.
Hindustan Zinc has actively participated in COP26 Business Working Group. The partnership underscores our firm commitment to working with trade associations to formulate a new set of guidelines for effective transition to a low-emissions and climate-resilient future.
Hindustan Zinc joined the IZA Climate Change Task Force, actively participating in characterising the carbon footprint of recycled content in SHG zinc production. The partnership is also aimed to drive societal benefits of increased resource recovery in a circular economy.
Hindustan Zinc has partnered with CII’s Working Group on Driving Accelerated Climate Action by Indian Businesses and with Confederation of Indian Industry (CII) on webinar series ‘Race to Zero’ structured around sessions on EP 100 (Energy Productivity), SME Climate Hub, RE 100 (Renewable Energy), EV 100 (Electric vehicles) and Technology Transfer. Around 200 participants from different industries took part in each of these sessions.
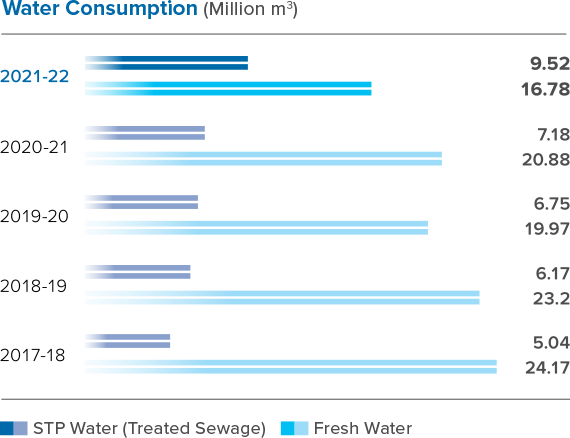
A growing population and the increase in extreme weather events due to climate change, underscores the urgency of managing our water impact more efficiently. This mandate assumes even greater criticality while operating in a water scarce area.
We believe that water is a shared resource, vital to sustaining biodiversity, populations and their economic prosperity. We believe that by cutting down on freshwater intake across our operations, and protecting water quality, we can reduce our environmental footprint and ensure sustained community and stakeholder support.
Our commitment to water stewardship is manifest in our efforts to use water prudently, maintain water quality, and engage with communities to collaboratively manage a shared water resource.
Development of sustainable resources is central to our ESG strategy. As part of our long-term commitment to water stewardship, we are focussed on:
To manage our water impacts efficiently, we first need to understand the specific risks at our operating sites, as well as our overall impact on water resources. To this end, we have conducted a detailed water risk assessment across Hindustan Zinc. The objective of this study was to conduct a sensitivity analysis and stress testing for water-related risks and calculate an apt water pricing structure for the Company. There are various tools available for undertaking such an assessment from which we have used WBCSD’s India Water Tool, WRI Aqueduct and GEMI local water tools, among others, for our study.
Using these tools, we have identified and assessed risks and worked out a management strategy. An analysis of the futuristic scenario by Aqueduct Water Risk Atlas showed that the indicators for water stress are high in most of our locations. Regardless of the level, however, we apply rigorous standards and processes to manage risks.
With our operations located in areas with varying degrees of water stress, we follow a four-way approach to manage our water resources and reducing our dependencies on fresh water. Led by our strong focus on water consumption and management, we have adopted a water management policy that commits us to recognise the social, economic, and environmental value of water, in the context of the global concern of water scarcity.
Approach

We are committed to zero liquid discharge across our locations. During the year, the Debari zinc smelter successfully commissioned a 3,000 kilolitre per day (KLD) zero liquid discharge ZLD plant. The move is aligned with our vision of ‘Zero Harm – Zero Waste – Zero Discharge’. We are striving to develop sustainable social solutions for a greener future by strengthening our zero discharge.
The newly installed RO-ZLD plant recycles processed water, which is then reused in operations, enabling complete utilisation of the wastewater, which ensures that there is no discharge. The salt generated can also be reused in the leaching process in place of the commercial sodium sulphate being used currently.
We plan to commission ZLD plants at all our units and remain committed to principles of water conservation and zero discharge. Expansion of 3,200 KLD ZLD plant at Dariba Smelter is under progress and shall be commissioned by Q2 of FY 2022-23. At Zawar Mines (ZM) and Rampura Agucha Mine (RAM) too, ZLD projects of 4,000 KLD capacity each have been initiated to improve recycling and strengthen the zero discharge. Like ZM, a dry tailing plant at Rajpura Dariba Mine (RDM) is also in the final stage of commissioning. It will result in significant amount of water recovery from the tailing.
With these RO-ZLD Plants, we will be able to increase water recycling and minimise fresh water usage, as this waste water is evaporated in solar evaporation pond so far to maintain Zero Liquid Discharge status. Our ZLD projects and dry tailing plants helped us scale our water recycling by 44% in FY 2021-22 from 39% in the previous fiscal.
In consonance with our focus on enhancing ground water recharge through rainwater harvesting projects, we have created an estimated recharge potential of 8.7 million cubic metres per annum of rainwater, covering 84 ponds in 43 villages near the Rampura Agucha Mine location. Through 358 recharge structures, it is expected to increase the availability of good-quality groundwater in the area, resulting in sustainable water availability for various purposes, besides securing the livelihood of villagers.
The initiative is estimated to benefit 70,000-75,000 people living in this area. As a result of the project, crop patterns and yields will also increase.
We are also committed to build rainwater harvesting structures in nearby villages, to make them water sufficient. These efforts are targeted to multiply the benefits of our operations in society and put Hindustan Zinc on track to become 5 times water positive by 2025.


Tackling Excess Water Consumption
Undertaking real-time water mapping
As part of the Initiative:
Benefits
This is a pilot project that is being implemented in one unit only

Responsibly managing waste from mining operations is crucial to ensure business sustainability. Any failure in tailing management can result in disaster, and hence, it is essential to communicate to stakeholders’ details of our tailing storage facilities and how we manage them. Hindustan Zinc has implemented global leading practices in tailing dam management, and we are associating with renowned global experts to provide long-term monitoring and advice on the design, construction, and operation of our three tailing storage facilities. Overall good construction quality, along with upgradation of tailing slurry transport and discharge lines through installation of piezometers (and inclinometer) with automated data collection and web-based monitoring, make it world-class.
We recognise the impact of mine tailing and tailing facilities on the environment, nearby communities, and other stakeholders. We are taking extensive measures for construction, operation, maintenance, and closure of facilities that mitigate the risk of tailing dam failure. We incorporate the best available technologies as guided by Vedanta’s Tailing Management Facility Standard. Wherever possible, we repurpose tailing materials and waste rock as backfill to stabilise our underground mining operations. Remaining tailing are then placed in a specially designed tailing storage to minimise the environmental, social, and economic risks.
Tailing management plans are an essential prerequisite for sound storage practice, as most failures of tailing storages around the world result from inadequate management of the storages. Effective implementation of a management plan not only results in a safer tailing storage facility (TSF) but will frequently reduce overall costs associated with operation and closure of the facility.
All our operating mines have a Tailing Management Plan – an Operations, Maintenance and Surveillance (OMS) manual. It describes
Safe and responsible management of TSF is central to our mining activities to ensure that a high standard of care is applied at the design, construction, operation, and closure stages of mining. Additionally, we are committed to continually improve the management of our facilities by developing and incorporating best practices like:

Our facilities are regulated, permitted, and have been managed for many years to comply with local laws, regulations, permits, licenses, and other requirements. Our internal assurance processes verify that our managed TSFs operate in accordance with the Vedanta standard and also in alignment with Global Industry Standard on Tailing Management. Our operational TSFs have emergency response plans – tested through training exercises in collaboration with stakeholders. They follow strict business resilience and communication protocols.
Clean air is critical to health. Across the business, we continue to pursue improvements to air quality management for our host communities and of surrounding ecosystems. We have focussed on reduction of emissions of particulate matter, as well as gases emitted by our operational activities, including mining, materials handling, processing, and transportation.
Hindustan Zinc is committed to measure, control, and reduce air emissions at each of its sites. We have implemented systems and procedures to address the concerns of local communities besides complying with the conditions of environmental licence. Through advanced mitigation, measurement, and management strategies, we continue to identify, reduce and, wherever possible, eliminate potential impact to air quality by improving operational processes and increasing awareness. We have installed online emission monitoring systems, connected directly to the servers of the Pollution Control Board.
Our emphasis is on prevention and management of air quality through operational discipline and process improvement.
As part of our sustainable development focus, we continue to invest in the protection and enhancement of the biodiversity around our operations. There is in place a unique and exclusive Biodiversity Management Plan (BMP) for all our operations. Our dedicated Biodiversity Policy and Management Standard advises on ways to avoid, minimise, and compensate for disruption to flora and fauna, from project scoping to site closure and beyond.
We are working towards a minimum of No Net Loss (NNL) of biodiversity and Net Positive Gain (NPG) of biodiversity (for a critical habitat) at all our operations. Our biodiversity management initiatives include an afforestation programme, Biodiversity Risk Assessment, restoration of exhausted waste dump, conservation of schedule-1 fauna species, awareness, and partnership.
We are working in partnership with NGOs, international institutions, and governments to advance our biodiversity agenda and gain expert insights. We have joined the Taskforce on Nature related Financial Disclosures (TNFD), which is committed to facilitate action and reporting on evolving nature-related risks.

To integrate conservation of biodiversity and ecosystem services into Hindustan Zinc and enhance the Company’s performance in biodiversity conservation and management, we have engaged with International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) for three years with the following objectives:

“The formation of a Board-level ESG and Sustainability Committee accentuates Hindustan Zinc’s aspiration to be a leader in ESG across the key metrics of business operations, community care and employee safety & wellbeing. Coupled with other ESG-centric initiatives undertaken during the year, this underscores our unwavering commitment towards creating a positive environment through a vision of Zero harm, Zero waste and Zero discharge. Our initiatives towards ensuring safe functioning across our operations and facilities are crafted to strengthen the organisation-wide safety framework for critical risk management and improving industrial hygiene. The various ESG-related awards and accolades we received during the year encourage us to move aggressively forward towards achieving our Sustainability Goals 2025 and creating long-term value for our stakeholders. We are pledged to conducting our business in a socially responsible and ethical manner, respecting our employees, our communities, our business partners, and all stakeholders.”
Pradeep Singh Chief HSE Officer
Hindustan Zinc follows the principle of reducing waste, quantitatively and qualitatively, through recovery and recycle. To ensure recycling of the waste in the landfills, Jarofix Yard phase 2 at CLZS has been partially restored with Mycorrhiza technology in partnership with TERI (The Energy and Resources Institute). The project is aimed at reclamation of 6.25 hectares of wasteland into productive land by increasing the green cover, enhancing biodiversity, controlling fugitive dust emissions, and restoring the site. It also makes plants less vulnerable to environmental stresses through optimum use of water resources.
Miyawaki is a technique pioneered by Japanese botanist Akira Miyawaki, which helps build dense, native forests. The approach is supposed to ensure that plant growth is 10 times faster and the resulting plantation is 30 times denser than conventional landscapes and tree plantation. It involves planting dozens of native species in the same area, which becomes maintenance-free after the first three years. These forests, which are full of biodiversity, retain groundwater, thus recharging the groundwater table. They attract more birds, produce native fruits, and improve the aesthetics as well. This technique of growing Miyawaki forests is completely chemical-free and sustains itself while supporting local biodiversity. We have successfully implemented a pilot project at Zinc Smelter Debari and will replicate it across all our units.
1 Acre (0.4 hectares) area in Debari colony developed through this technique, with nearly 50 types of native species and 8,000 plantations.